Learning Basic Elements Of HTML...(<h>, <p>, <img>, <a>)
Introducing Basic HTML Tags.
Table of contents
No headings in the article.
- INDEX:
- 1) What are HTML Tags?
- 2) Why HTML Tags are important?
- 3) Learning basic HTML Tags
WHAT ARE HTML TAGS?
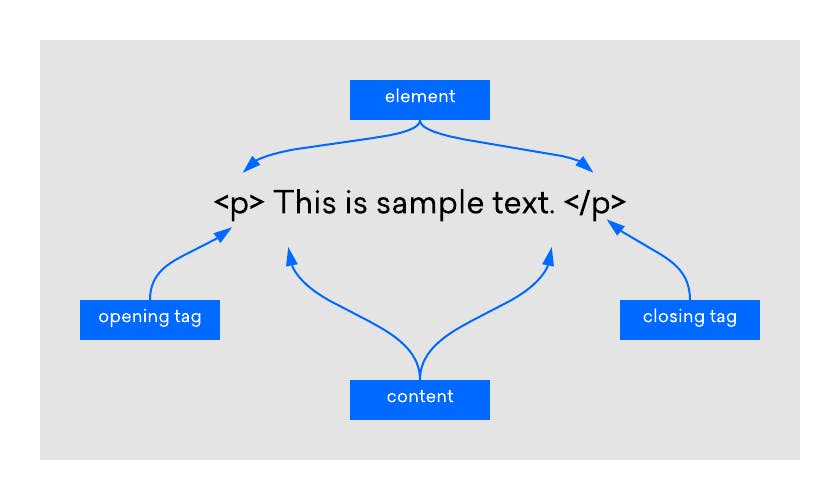
HTML tags are like keywords which defines that how web browser will format and display the content. With the help of tags, a web browser can distinguish between an HTML content and a simple content. HTML tags contain three main parts: opening tag, content and closing tag. When a web browser reads an HTML document, browser reads it from top to bottom and left to right. HTML tags are used to create HTML documents and render their properties. Each HTML tags have different properties.
An HTML file must have some essential tags so that web browser can differentiate between a simple text and HTML text. You can use as many tags you want as per your code requirement.
All HTML tags must be enclosed within < > these brackets. Every tag in HTML performs different tasks. If you have used an open tag , then you must use a close tag (except some tags).
WHY HTML TAGS ARE IMPORTANT?
HTML tags are bits of code that can be used to describe our content to search engines. We can use HTML tags to highlight the important parts of our copy, to describe images, and even to give instructions to search engine bots. HTML tags are also used to influence the way our pages appear in search results.
LEARNING BASIC HTML TAGS ONE BY ONE-
<h1>, <h2>, <h3>, <h4>, <h5>, <h6>
indicating six levels of section headings, in that <h1> indicates top level of section heading and <h6> indicates bottom level of section heading.
<p>
indicating a paragraph. In that <br> is indicating to change line of any paragraph from any word.
<img>
The <img> HTML elements embeds an image into the document.
<a>
creates a hyperlink to web pages, files, email addresses, locations in the same page or anything else a URL can address.
<link>
specifies relationships between the current document and an external resource.
<title>
element defines the document's title that is shown in a Browser's title bar or a page's tab. It only contains text; tags within the element are ignored.
<html>
element represents the root (top-level element) of an HTML document, so it is also referred to as the root element. All other elements must be descendants of this element.

